Neural Networks Explained Simply
Neural networks are the technology that makes modern AI possible.
They power language models like ChatGPT, image generators, voice AI, and many other systems we use every day.
In this lesson, you will learn:
• What a neural network is (in plain language)
• How it works step by step
• Why it has “layers”
• Real examples to understand it
• Key terms explained simply
• A short practice exercise
By the end, you will understand the core idea behind today’s AI systems — without math or complex programming.
What Is a Neural Network? (Simple Definition)
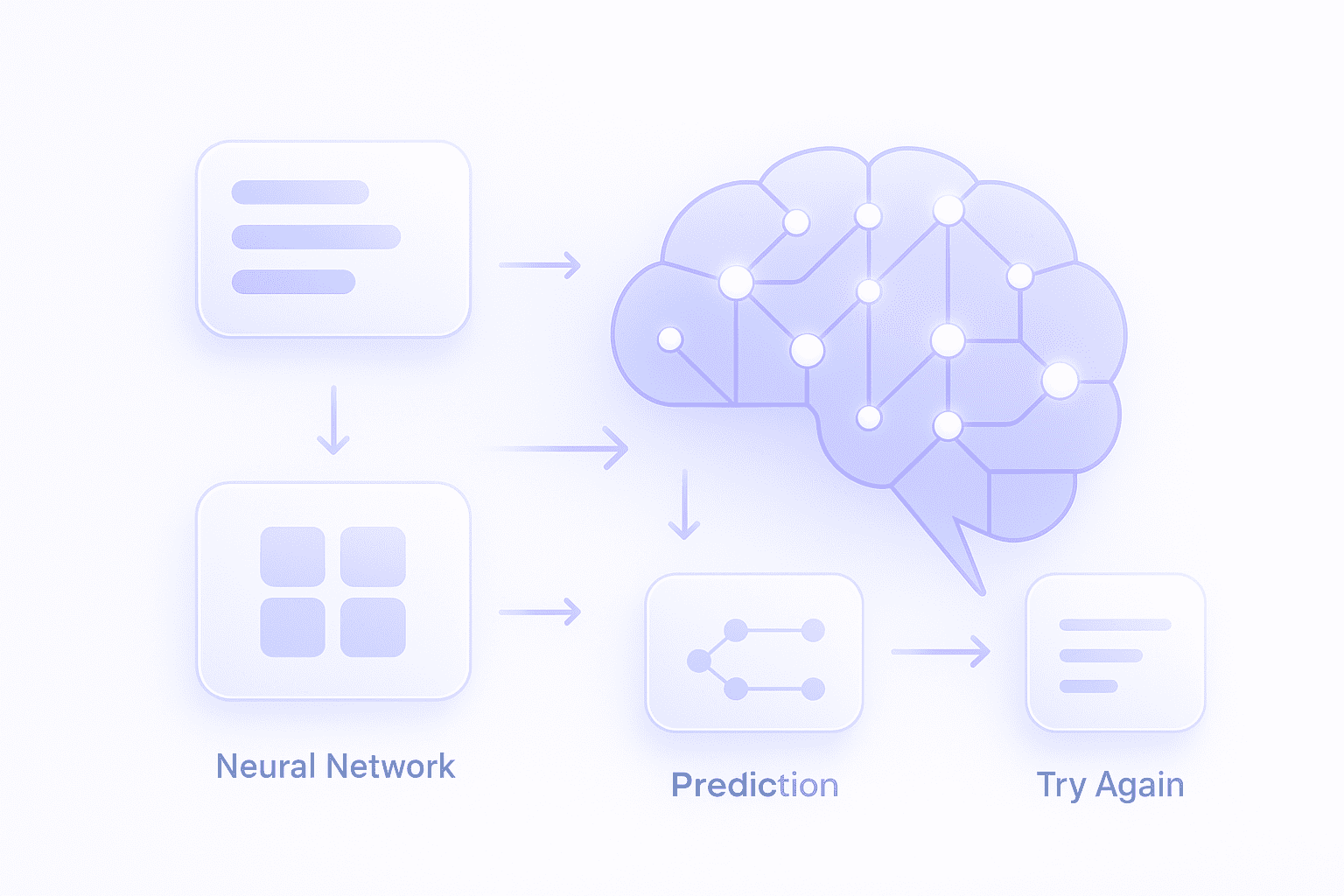
A neural network is a computer system that learns by passing information through small connected units called nodes, similar to how neurons connect in the human brain.
It does not think like a human,
but it copies the idea of learning by connection and improvement.
Think of it like this:
• Each node = tiny decision maker
• Thousands of these nodes work together
• They pass information to each other
• With practice, they get better at predicting answers
Why Neural Networks Exist
Old computer programs followed strict rules.
Neural networks introduced learning.
Traditional programs:
“If this happens, do that.”
Neural networks:
“Learn from examples, then make decisions.”
This allows AI to:
• Recognize images
• Understand speech
• Answer questions
• Translate text
• Predict results
• Generate content
That is why neural networks changed AI forever.
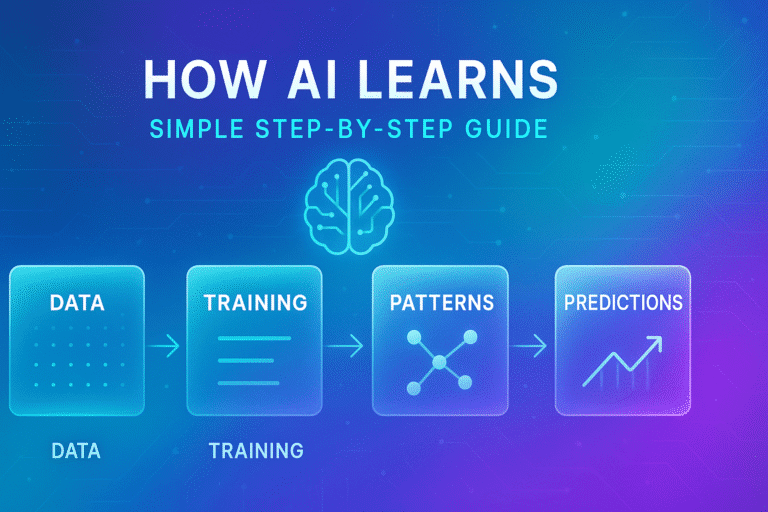
How a Neural Network Works (Simple Steps)
1) AI Receives Input
The input is the information the AI needs to learn from.
Examples:
• Text
• Image pixels
• Voice recording
• Numbers
2) Input Passes Through Hidden Layers
Hidden layers are where learning happens.
Inside these layers:
• Nodes check input
• They make tiny decisions
• Each pass adjusts accuracy
• Errors get corrected
• Layers repeat until patterns are found
More layers = deeper learning
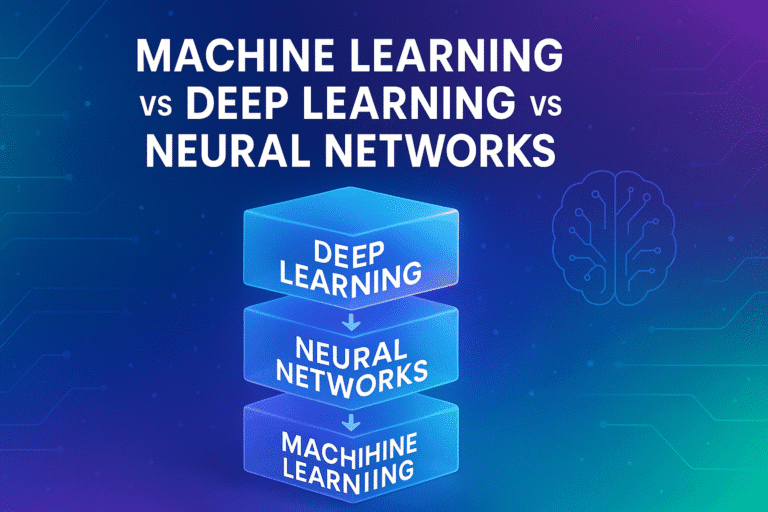
This is why it’s called deep learning.
3) AI Produces Output
After learning, the network gives a result.
Examples:
• Text answer
• Identified image (cat, car, tree)
• Translated language
• Predicted number
Simple Visual Explanation
You will create this diagram later:
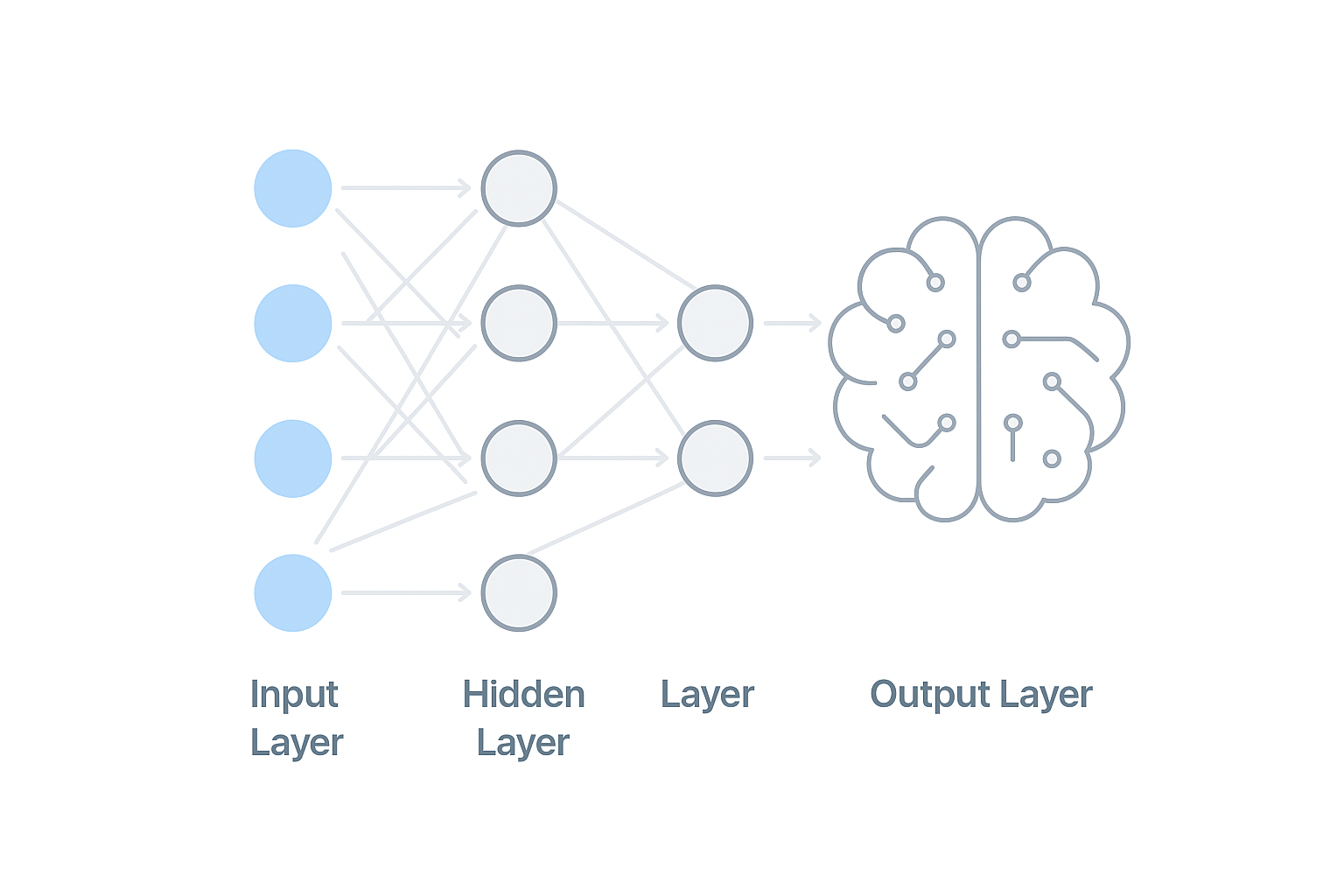
Input → Hidden Layers → Output
Like a tunnel:
Information goes in → gets refined → correct answer comes out
A Real-Life Example: Handwritten Numbers

Example problem: recognize handwritten digits (0–9)
• Input = image of number
• Hidden layers = detect curves, angles, shapes
• Output = “This is number 8”
The network learns patterns in handwriting
(some people write messy — AI learns anyway)
Another Example: Cat vs Dog Recognition
Input: photo
• Hidden layers: detect ears, fur texture, face shape
• Output: “Cat” or “Dog”
The network does not “see” like humans
It learns shapes, edges, textures mathematically.
Why Neural Networks Need Data
To learn patterns, neural networks need many examples.
More data = better predictions
Wrong data = wrong learning
Just like students:
more practice = better understanding.
Key Terms Explained Simply
| Term | Simple Meaning |
|---|---|
| Neuron / Node | Small learning unit in AI |
| Layer | Group of nodes doing a learning step |
| Input layer | Where information enters |
| Hidden layer | Where learning happens |
| Output layer | Final answer made by AI |
| Weights | Internal settings AI adjusts to improve |
| Training | Practicing with examples |
| Inference | Using what AI learned to answer |
Why Neural Networks Work Well
They can:
• Handle huge amounts of information
• Learn complex patterns
• Improve with more training
• Solve problems humans struggle with
• Run fast once trained
That’s why they’re used everywhere — from phones to self-driving cars.
Neural Networks vs Human Brain (Simple Comparison)
| Human Brain | Neural Network |
|---|---|
| Learns with meaning & emotion | Learns with data & math |
| Flexible understanding | Pattern-focused |
| Slow learning but deep understanding | Fast pattern recognition |
| Creative + emotional | No real understanding or emotion |
AI learns patterns, not meaning.
Common Misunderstandings
Misconception: Neural networks understand the world
Truth: They recognize patterns, they do not understand life
Misconception: More layers always means smarter AI
Truth: Quality of data and training also matter
Misconception: Neural networks think like brains
Truth: They only copy the connection idea, not real thinking
Mini Exercise (Practice)
Write simple answers to solidify learning:
• What goes into the input layer?
• What happens in hidden layers?
• What comes out in the output layer?
• Name one real-life use of neural networks.
This builds understanding — not memorization.
Quick Recap
Neural networks:
• Learn patterns from data
• Pass information through connected layers
• Correct mistakes and repeat
• Provide predictions or answers
• Power modern AI systems like ChatGPT and Google Lens
They are not brains — they are pattern machines.
FAQ
Why are they called neural networks?
Because they mimic how neurons connect in the brain.
Do neural networks think?
No. They detect patterns and make predictions.
Is deep learning the same as neural networks?
Deep learning is neural networks with many layers.
Are neural networks always needed?
No. Some simple AI uses basic algorithms.