How AI Learns: Simple Step-By-Step Guide
Artificial Intelligence may look complex, but the learning process behind it can be understood in simple steps.
The goal of this lesson is to explain how AI actually learns, using clear language and practical examples.
By the end of this article, you will understand:
• What AI learning really means
• Why AI needs large amounts of data
• The training process step-by-step
• Real-world examples (not technical)
• Key terms explained in simple words
• How AI improves accuracy over time
This is your first foundation lesson in learning AI in a simplified, structured way.
What Does “Learning” Mean in AI?
When humans learn, we understand meaning and connect ideas.
AI does not understand like humans.
AI learns patterns from examples and uses math to make predictions.
AI learning means:
• It sees many examples
• It finds patterns
• It creates rules from patterns
• It predicts new answers based on those rules
• It improves by adjusting mistakes
Example idea:
If you show many dogs to a child, they learn what a dog looks like.
AI does the same — just without understanding emotion, purpose, or meaning.
Why Data Is Important in AI Learning
AI learns through data the same way students learn through textbooks and practice questions.
More data = better learning
Better data = more accurate AI
Types of data AI learns from:
• Images
• Text
• Numbers
• Audio
• Video
If the data is poor or biased, AI will learn incorrectly.
So the quality and variety of data are key.
How AI Learns: Step-By-Step Process
Step 1: Collect Data
AI needs examples to learn.
Companies collect data from:
• Public information online
• Databases
• Images and videos
• Text documents
• User interactions
The more diverse the data, the smarter the AI becomes.
Step 2: Label or Organize Data
Sometimes humans help AI learn by labeling data.
Examples of labels:
• A picture marked “cat”
• An email marked “spam”
• A review marked “positive” or “negative”
Labeling helps AI understand what is correct.
Step 3: Train the Model
Training is like practice.
AI studies data repeatedly until it can recognize patterns.
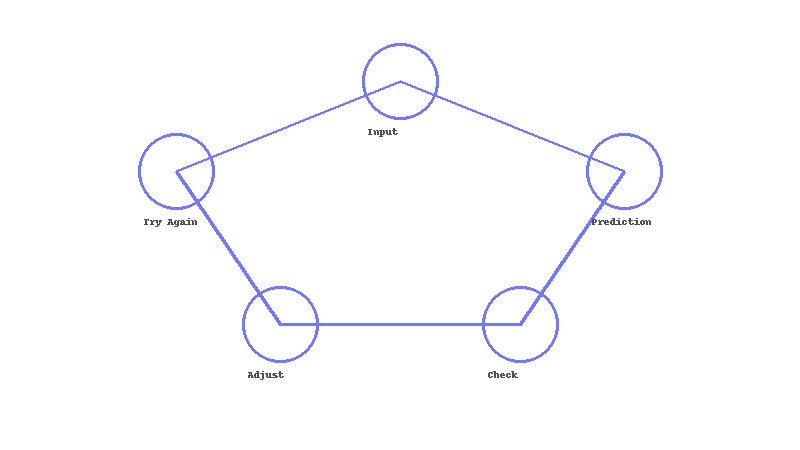
During training, the model:
• Looks at examples
• Tries to guess the right answer
• Gets corrected
• Adjusts and tries again
• Repeats many times
This repetition makes the AI stronger and more accurate.
Step 4: Test the Model
Once trained, AI is tested with new unseen data to check how well it performs.
Testing checks:
• Accuracy
• Confusion or errors
• Bias
• Weak areas
If results are weak, training continues.
Step 5: Improve and Tune
AI improves through:
• More training rounds
• Better data
• Adjusting internal settings
• Fixing errors
Just like humans revise topics they got wrong in a test, AI repeats and improves too.
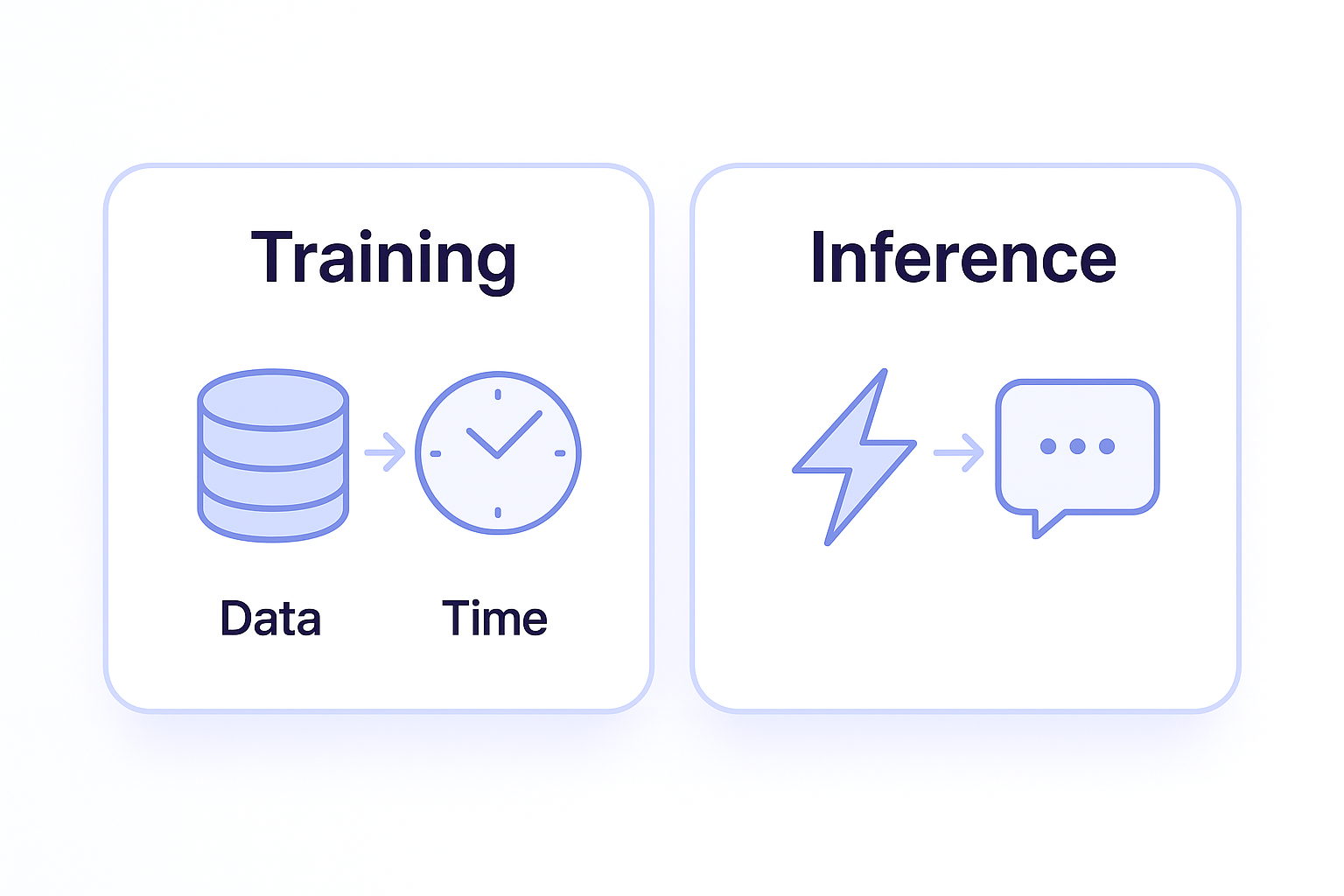
Training vs Using AI (Key Difference)
People often mix these two up:
Training AI
• Long process
• Needs huge data and computers
• Expensive and time-consuming
Using AI (Inference)
• Quick responses
• Happens when you ask a question
• Does not require big computers locally
When you open ChatGPT and type a question, you are not training it, you are using the trained model.
Real-Life Learning Examples
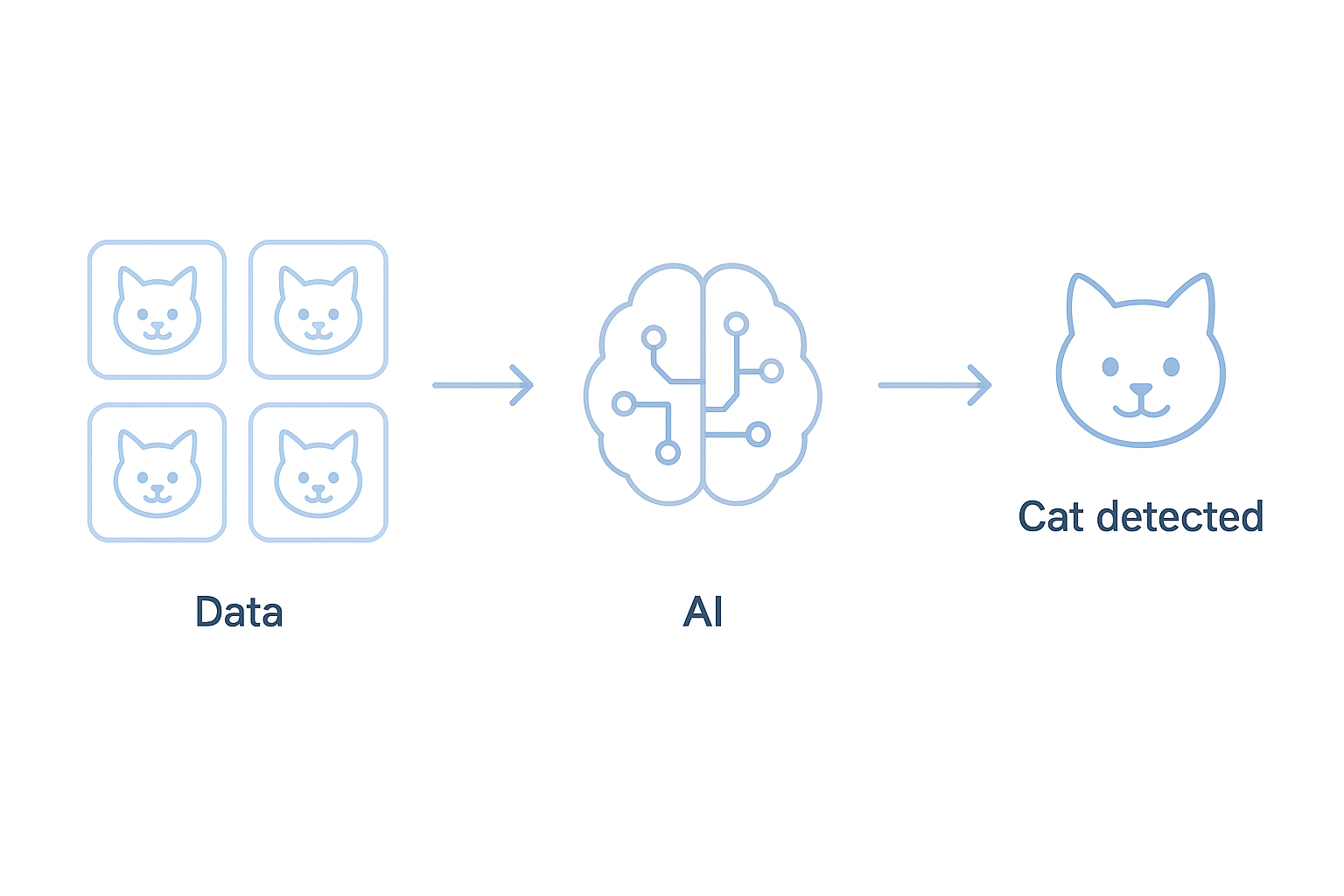
Example 1: Cat Detection
AI sees thousands of cat pictures and learns:
• Shape patterns
• Ears, whiskers, eyes
• Fur texture
• Tail shape
Next time it sees a new picture, it predicts, “This is a cat.”
Example 2: Spam Email Detection
AI scans many emails marked as spam and non-spam.
It learns patterns like:
• Suspicious phrases
• Fake links
• Sender behavior
Then filters spam automatically.
Example 3: Voice Assistants
AI learns speech patterns from millions of voices.
It identifies:
• Words
• Accent
• Tone
That’s why Siri and Google Assistant can understand different people.
How AI Improves Over Time
AI improves by:
• Getting more training data
• Receiving better feedback
• Updating models (versions)
• Correcting mistakes
• Running more training cycles
The improvement is continuous — like leveling up in games or improving writing skills through practice.
Important Terms Explained Simply
Term: Model
Meaning: The trained AI brain that makes predictions
Term: Dataset
Meaning: The collection of examples used for training
Term: Training
Meaning: Teaching AI with examples and corrections
Term: Inference
Meaning: AI using its training to answer questions
Term: Accuracy
Meaning: How often AI gives the correct answer
Term: Bias
Meaning: Wrong learning due to limited or unfair data
Common Misunderstandings
Misconception: AI thinks like humans
Truth: AI identifies patterns and outputs predictions
Misconception: AI learns instantly
Truth: Training takes time and resources
Misconception: AI understands meaning
Truth: AI works mathematically, not emotionally
Practice Exercise
Try this for your own understanding:
• Describe how AI learns in 2–3 sentences
• Give one example of AI learning in real life
• Explain the difference between training and using AI
Writing it helps build true understanding — not memory only.
Mini Quiz
• Why does AI need data?
• What is training?
• What is inference?
• Does AI “understand”? Why or why not?
This self-check strengthens learning.
Summary
AI learns by:
• Studying examples
• Finding patterns
• Testing predictions
• Fixing mistakes
• Repeating the cycle
It does not think like humans — but it can analyze patterns far faster.
This is the foundation of how AI systems like ChatGPT, Google, and image-recognition tools work.
FAQ
Does AI learn forever?
It learns until training stops, then improvements are done in updates.
Can AI learn by itself?
AI needs data and feedback. It cannot learn without input.
Is AI training dangerous?
Training itself is not dangerous. Misuse of AI is the risk, not learning.
Can small data train AI?
Small data works for simple tasks, but advanced AI needs massive data.